Maintenance Management
Plan, schedule and carry out detailed equipment maintenance work orders. Efficiently track service work from start to finish on the go with the Mobile App. This guide will walk you through the setup process, as well as the step-by-step actions for service persons to log maintenance details.
- Maintenance Work Order Types
- Maintenance Scheduling Types
- Security
- How to Create Maintenance Work Order
- How to Log Maintenance
- How to Check In Serviced Equipment
- How to Create Maintenance Type
- How to View the Maintenance History of a Tool
- Scheduling Preventive Maintenance
- Bulk Upload
Maintenance Work Order Types:
ToolWorks supports two types of maintenance work orders: Standard and Advanced.
Standard Maintenance Work Orders (Default)
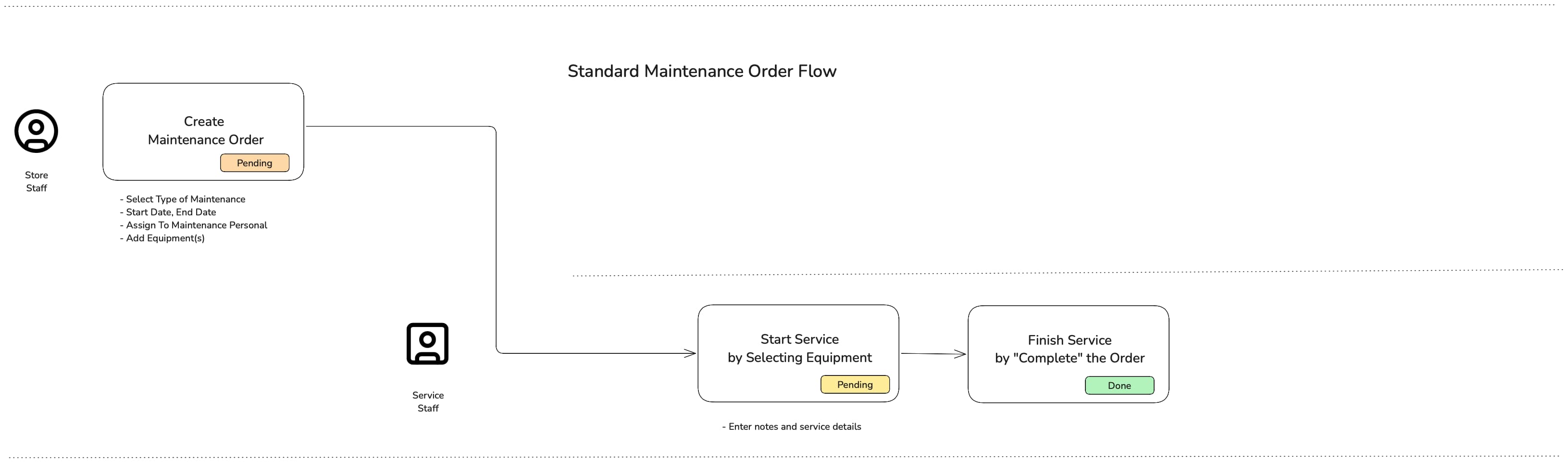
Standard maintenance work order allows you to schedule tools and equipments for maintenance, get notification of upcoming maintenance and track/note work done. You can choose to include or exclude service personnel and there is no transfer of tools custody to the service personnel. When you create a Standard maintenance work order, it starts in a Pending state (scheduled/work to be done). When the maintenance work is completed, it moves to the Completed state.
Advanced Maintenance Work Orders with Transfer Custody
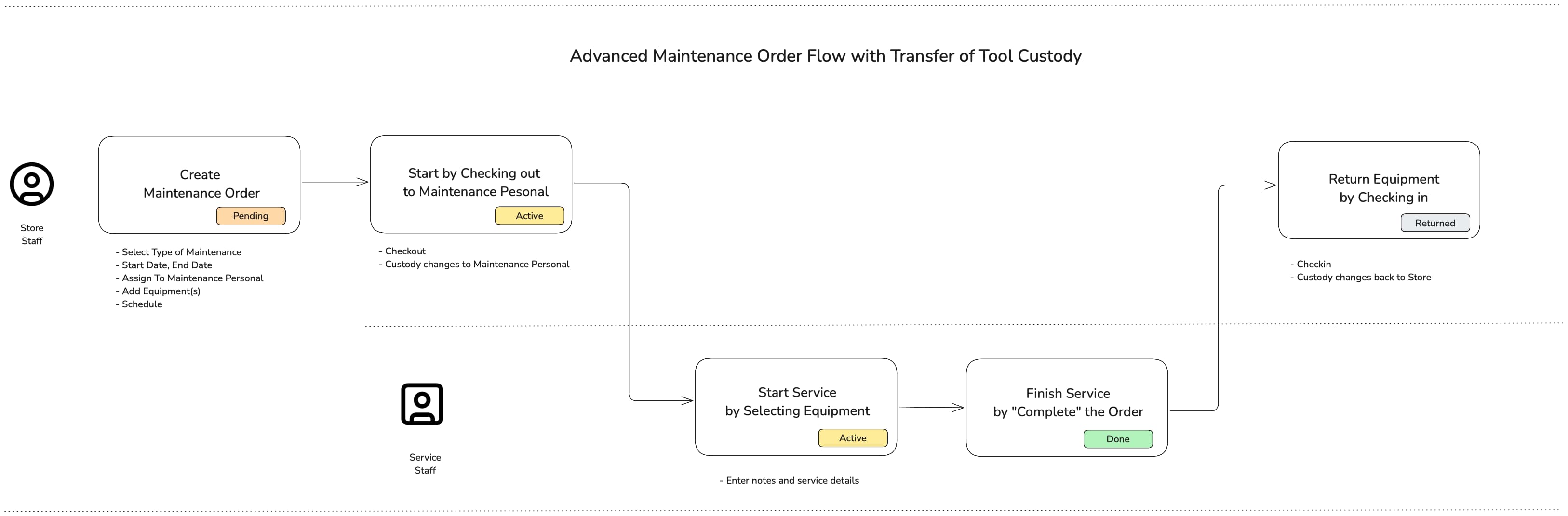
Advanced maintenance work order adds tool transfer custody workflow to the Standard maintenance work order. With advanced order, the service personnel must be assigned to perform the maintenance and assets will be checked out to the service personnel. When the maintenance work is done, order moves to the Completed state. You must check in assets to finish the maintenance work. Order goes through Pending (scheduled), Active(tools checked out to service person), Completed(service done) and Returned(tools checked in) states.
Advanced maintenance work orders are available for Enterprise customers.
Maintenance Scheduling Types
The system offers three distinct scheduling methods, each designed to address specific maintenance needs and scenarios.
Date-Based Maintenance
Date-based maintenance scheduling allows you to establish regular maintenance intervals based on calendar time. Enterprise users can choose between fixed interval scheduling, where maintenance tasks occur at set dates regardless of usage, or dynamic scheduling that automatically adjusts based on completion dates of previous maintenance work. This flexibility ensures that maintenance schedules align with actual equipment needs and operational patterns.
The system's smart scheduling algorithm considers factors such as resource availability, operational schedules, and maintenance history to optimize timing. Email notifications keep relevant team members informed of upcoming maintenance tasks, ensuring nothing falls through the cracks.
Meter-Based Maintenance
For equipment where usage patterns matter more than calendar time, ToolWorks offers sophisticated meter-based maintenance scheduling. This feature is particularly valuable for vehicles, heavy machinery, and equipment where wear is directly related to usage hours or mileage.
The system continuously monitors usage metrics and automatically triggers maintenance alerts when equipment approaches predetermined thresholds. This precise approach ensures that maintenance occurs exactly when needed, neither too early (wasting resources) nor too late (risking breakdowns).
Automated Return-Based Maintenance
ToolWorks introduces an innovative approach to maintaining equipment that sees extended periods of use. The system automatically schedules maintenance inspections when tools or equipment are returned after long-term deployments. This ensures that heavily used equipment receives necessary attention before being redeployed, preventing the accumulation of wear and tear that could lead to failures.(Enterprise Feature)
Security
- In order to create maintenance order, user must have the Create Maintenance Order right.
- In order to service the equipment, user must have the Service Maintenance Order right.
For Store Staff/Administrators:
💡 You must have the right Create Maintenance Order to perform this action.
How to Create Maintenance Work Order
- Navigate to the Tools tab. [shift-t]
- Locate tools and/or equipments that need maintenance and click
Add To Cart. - In the Cart, Click
Maintainto create maintenance order and enter the details.
- Select Type of Maintenance
- Select Based On. You can choose to schedule maintenance based on Date (Duration) or Meter (mileage or hours). Enterprise customers can also choose Return to auto schedule maintenance when tool is returned.
- For Date based, enter Start and End dates. For Meter based, enter Meter Type and When to Trigger Service (mileage/hours count).
- Enter Expected Days For Service to complete maintenance (optional)
- Maintenance By, assign user that will perform the service (optional)
- Enter notes for maintenance personnel (optional)
- Click
Scheduleto schedule maintenance order. For Advances Orders, you can also clickCheck Outto assign equipment custody to user and start the work order.
👉 If order start date is more than 3 days in future, Schedule is automatically highlighted for Orders with transfer custody.
For Maintenance Staff
💡 User must have the right Service Maintenance Order to perform this action.
How to Log Maintenance
- Navigate to the Maintenance screen.
- Open the assigned work order and select Tool to start working.
- Enter notes about service performed on tool
- Save
- When done with all equipments, click
Completeto indicate maintenance completed.
🤖 Using Copilot
- Describe what maintenance was done on the tool (please mention tool barcode)
- Copilot will record maintenance details and auto
Completethe work order.
For Store Staff/Administrators
How to Check In Serviced Equipment (Advanced Orders)
- Navigate to the Maintenance screen.
- Open the assigned work order.
- You can enter notes for each service equipment (and update its status).
- You can also attach documents. Just drop documents in the Documents upload panel (or click to browse and select for File Explorer).
- Click
Check Into indicate maintenance completed and equipment return to inventory.
How to Create Maintenance Type
- Navigate to the Maintenance screen.
- Click
Maintenance Types - Click
Add. - Enter following details
- Name
- Description
- Additional optional notes
- Click
Addto save to create new maintenance type. - Located newly created maintenance type and
Clickto view details ExpandCustom Task List- Click
Add Custom Task
- Add one or more Custom Fields to track maintenance details
- Click Save when done
- Click Update to save changes to custom fields.
💡 User needs the right Define Context Scoped Custom Field to create custom tasks. Custom Fields for Maintenance feature is available for Enterprise customers.
How to View the Maintenance History of a Tool
You can view historical maintenance and future schedule details by on the Maintenance tab for a Tool Inventory.
- Navigate to the Tool tab. [shift-t]
- Locate the Tool for which you want to view maintenance history.
Clickthe Tool to view tool inventory details.Selectthe Maintenance tab to view maintenance history.
Scheduling Preventive Maintenance
Scheduling Preventive maintenance is a crucial part of maintaining your tool inventory. ToolWorks supports scheduling preventive maintenance for tracked equipments.
- Navigate to the Tools tab. [shift-t]
- Locate tools and/or equipments that need maintenance and click
Add To Cart. - In the Cart, Click
Maintainto create maintenance order and enter the details.
- Select Type of Maintenance
- Select Based On. You can choose to schedule maintenance based on Date (Duration) or Meter (mileage or hours). Enterprise customers can also choose Return to auto schedule maintenance when tool is returned.
- Enter Expected Days For Service to complete maintenance
- Assign User that will perform the service
- Optionally notes for maintenance personnel
- Add Tools/Equipments.
ExpandRecurrence.
For scheduling Preventive maintenance based on duration
-
Select Interval
-
Enter Interval Days. New order will be schedule every Interval days.(Think of it as repeat interval)
-
Optionally you can enter an end date to stop the recurrence.
-
There are two options as to when create Next Maintenance
- Schedule after completion of current work order. Think of it as relative start after maintenance is completed.
- Create ahead of time based on repetition interval. Think of it as absolute start, dates are fixed based on repetition interval.
For scheduling Preventive maintenance based on meter (mileage or hours)
- Select Meter
- Enter Interval Meter Count. New order will be schedule whenever Interval + last maintenance meter exceeds tool meter.
- Optionally you can enter an end date to stop the recurrence.
- There are two options as to when create Next Maintenance
- Select Schedule after completion of current work order. Think of it as relative start after maintenance is completed.
- Click
Schedule, to schedule service to be performed at a later date.
Note: For meter based maintenance, the Next Maintenance will be based on meter reading entered by user for the tool. When user updates meter, it checks if maintenance need to be scheduled.
For scheduling Preventive maintenance based on Return
- Select Upon Return
- Optionally you can enter an end date to stop the recurrence.
Auto Scheduling with Recurrence is available for Enterprise customers.
Bulk Upload
With Bulk upload of maintenance work orders, you can import past history and future schedule details. You can upload multiple maintenance orders at once with multiple tools. You will need to upload a CSV file with the following columns:
| Fields | Is Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Order Number | Optional | Number to assign to work order. This is optional, if you don't provide an order number, it will be auto-generated. It is required if you want to include multiple tools in the same order. Repeat the same order number to combine several rows into one work order. |
| Type of Maintenance | Required | Name of maintenance service to perform. |
| Maintenance By | Required | Email of person that performed or will perform the maintenance. |
| Status | Optional | Enter Pending for scheduled work orders. Enter Completed for regular completed order and enter Returned for advanced orders. Defaults to Pending. |
| Schedule Date | Required | Date when to perform maintenance. Date must be in YYYY-MM-DD format. |
| Return Date | Optional | Date when to maintenance is expected to be completed and tool returned. if not provided, schedule date will be used. Date must be in YYYY-MM-DD format. |
| Barcode | Required | Asset tag/barcode of tool |
| Quantity | Optional | Number of tools (defaults to 1) |
| Service Comments | Optional | Enter description of work performed. |
| Repeats | Optional | Enter Interval to repeat the maintenance at fixed interval or Meter to auto schedule maintenance based on meter update. |
| Interval Days | Required* | Number of days between each maintenance. *Required if you want to repeat. |
| End After | Required* | Number of occurrences. End After or End Date is *Required if you want to repeat. |
| End Date | Required* | End repeat by Date. Date must be in YYYY-MM-DD format. End date or End After is *Required if you want to repeat. |
| Next Maintenance | Optional | Enter Relative to schedule after completion of current work order or enter Absolute to created based on fixed repetition interval. Defaults to Relative. |
| Due By | Optional | Number of days after which maintenance is due. You can provide this or return date. |
| Transfer Custody | Optional | Enter Yes (or Y) to create advanced maintenance order with transfer custody workflow. |
| Interval Type | Optional | Enter 'MILEAGE' or 'HOURS' |
💡 You can download template file to start with from the Maintenance tab > Bulk Upload
Steps to Upload
- Navigate to the Maintenance tab. [shift-m]
- Click
Bulk Uploadand select CSV file to upload or drag and drop the file. - View the parsed file. Once you are satisfied with the data, click
Upload.
By following these step-by-step instructions, administrators can easily create and manage Maintenance work orders, while service personnel can seamlessly log maintenance details, streamlining the equipment maintenance operations and enhancing overall efficiency and accountability.
Help